Key Knowledge:
|
Evolution at its most fundamental level simply describes a cumulative change over time
- In living organisms, this involves a change in the heritable characteristics of a population between one generation and the next
Heritable characteristics are encoded for by genes and may be transferred between generations as alleles
- Hence biological evolution describes a change in the allele frequency of a population’s gene pool over successive generations

Gene Pools
A gene pool represents the sum total of alleles for all genes present in a sexually reproducing population
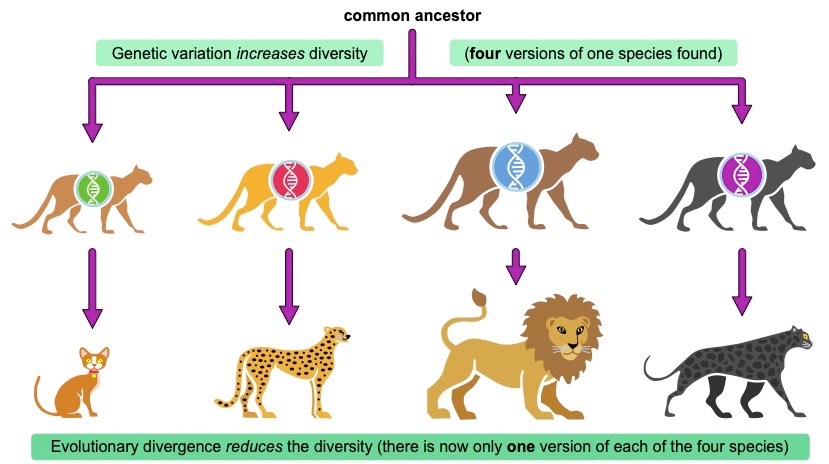
- A large gene pool indicates high amounts of genetic diversity, increasing the chances of biological fitness and survival
- A small gene pool indicates low amounts of genetic diversity, reducing biological fitness and increasing chances of extinction
Allele frequencies will change in a population over time (large populations with stable environments will experience less change)
- Genetic variation occurs naturally (via mutations) to increase the genetic diversity of a population by creating new alleles
- Evolutionary processes (e.g. natural selection) will decrease genetic diversity as species are adapted to suit the prevailing conditions