Key Knowledge:
|
A genetic cross is a means of determining the traits of potential offspring based on the genetic characteristics of the prospective parents
- A monohybrid cross determines the genotypes (and resulting phenotypes) of potential offspring for one gene only
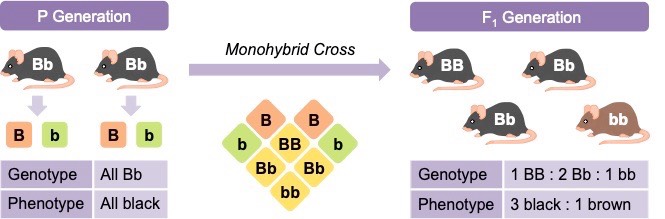
Monohybrid Cross
Monohybrid crosses can be calculated according to the following steps:
- Step 1: Designate letters to represent alleles (dominant = capital letter ; recessive = lower case ; co-dominant = superscript)
- Step 2: Write down the genotype and phenotype of the prospective parents (this is the P generation)
- Step 3: Write down the genotype of the parental gametes (these will be haploid and thus consist of a single allele each)
- Step 4: Draw a grid with maternal gametes along the top and paternal gametes along the left (this is a Punnett grid)
- Step 5: Complete the Punnett grid to determine potential genotypes and phenotypes of offspring (this is the F1 generation)
Test Cross
A test cross involves mating an unknown genotypic individual with a known homozygous recessive
- This is because recessive alleles will always be masked by the presence of dominant alleles
- Hence the phenotype of any offspring will reflect the genotype of the unknown parent
Test crosses can be used to determine whether a dominant phenotype is homozygous or heterozygous
- If the unknown parent is homozygous dominant, all offspring will express the dominant phenotype
- If the unknown parent is heterozygous, half the offspring should be dominant and half recessive
