Key Knowledge:
|
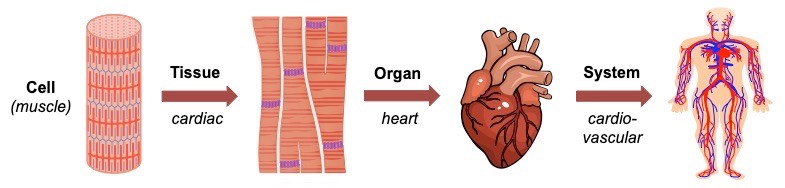
Multicellular organisms arise when groups of individual cells function together to form an interdependent collective entity
- Groups of structurally and functionally similar cells (and their intercellular materials) will assemble to form a tissue
- Different tissues may then interact to form a functional grouping known as an organ (e.g. heart, liver, etc.)
- Organs may cooperate to form complex organ systems (e.g. heart + blood vessels = cardiovascular system)
- The organ systems will collectively carry out the necessary life functions to sustain the complete organism
Multicellullar organisms are capable of completing functions that unicellular organisms could not undertake (i.e. emergent properties)
- This is due to the collective actions of individual cells combining to create new synergistic effects
- An example of an emergent property is the capacity for thought and emotion formed from the interaction of neurons in the brain