Key Knowledge:
|
Photosynthesis involves the synthesis of organic compounds (glucose) from inorganic molecules (CO2 and H2O) in the presence of light
- This process requires a photosynthetic pigment (chlorophyll) and can only occur in certain organisms (plants, certain bacteria)

Photosynthesis is a two step process:
- The light dependent reactions convert light energy from the Sun into chemical energy (ATP)
- The light independent reactions use the chemical energy to synthesise organic compounds (e.g. carbohydrates)
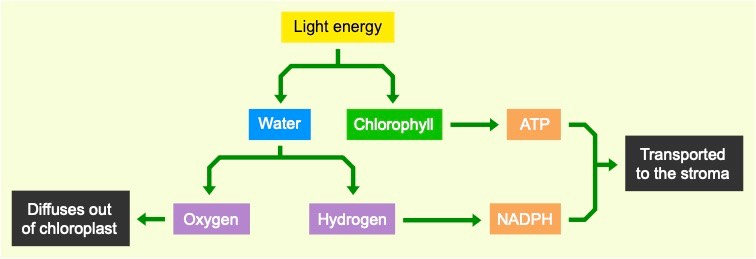
Light Dependent Reactions
The light dependent reactions occur within the membranous discs called thylakoids (which are arranged into stacks called grana)
- Light is absorbed by chlorophyll pigments (in photosystems), resulting in the release of energised electrons
- The electrons enter an electron transport chain, which results in the production of ATP (via photophosphorylation)
- Light is also absorbed by water, which is split (photolysis) to produce oxygen and hydrogen (carried by NADPH)
- The hydrogen and ATP are used in the light independent reactions, the oxygen is released from stomata as a waste product
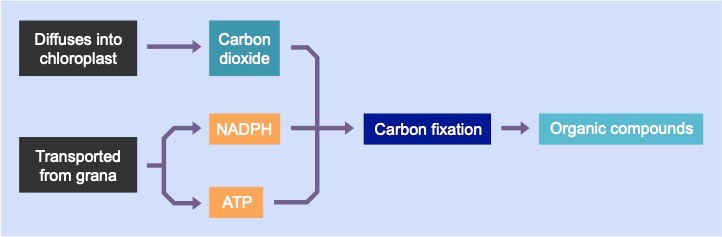
Light Independent Reactions
The light independent reactions occur within the fluid-filled interior of the chloroplast called the stroma
- ATP and hydrogen (carried by NADPH) are transferred to the site of the light independent reactions
- The hydrogen is combined with carbon dioxide to form complex organic compounds (e.g. carbohydrates, amino acids, etc.)
- The carbon is fixed by the enzyme Rubisco, with ATP providing the chemical energy required to join the molecules together
- This process is also commonly known as the Calvin cycle
Extension: Photophosphorylation
- ATP is produced in the light dependent stage via an electron transport chain, which is located on the thylakoid membrane
- As energised electrons (from chlorophyll) move through the chain, protons use the energy to translocate into the thylakoid lumen
- This creates an electrochemical gradient (or proton motive force) within the thylakoids
- The protons diffuse out of the lumen via a transmembrane enzyme (ATP synthase), which uses this movement to synthesise ATP
- Water replaces electrons lost from chlorophyll, while protons and de-energised electrons (i.e. hydrogen) are transferred to NADPH
Click to play video
Extension: The Calvin Cycle
- Carbohydrates (glucose, starch) are produced in the light independent stage via the Calvin cycle (in the stroma)
- A 5-C compound called RuBP is combined with carbon dioxide (using the enzyme Rubisco) to form a 6-C compound
- This 6-C compound is unstable and immediately breaks down into 3-C compounds called GP
- The GP is then converted into a triose phosphate (TP) using NADPH and ATP (from the light dependent stage)
- TP can be either used to synthesise carbohydrates or used to regenerate stocks of RuBP
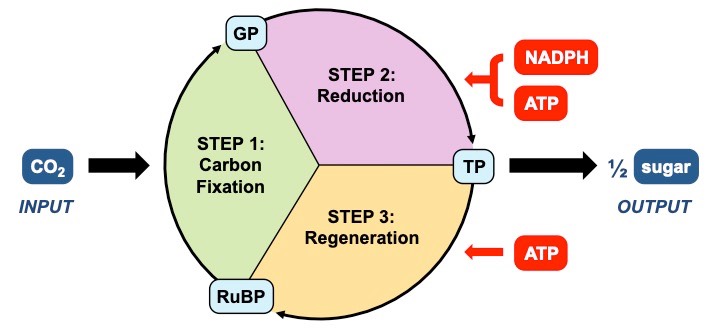
Balancing the Calvin Cycle:
The Calvin cycle must occur twice in order to produce a single molecule of glucose (sugar monosaccharide)
- Three molecules of RuBP (5C) are combined with three carbon dioxides to make six molecules of GP (3C)
- All GP molecules are converted into TP via the action of NADPH and ATP (intermediaries from the light dependent reactions)
- One TP is used to make a half-sugar, while the remaining five TP molecules are used to regenerate RuBP (5 × 3C = 3 × 5C)