Key Knowledge:
|
Evolution requires genetic variation among members of a species (to allow for the differential selection of heritable traits)
- Mutations function as a source of new alleles and (along with gene flow) increase the genetic diversity of a population
Mutations
A gene mutation is a change in the nucleotide sequence of a section of DNA encoding for a specific trait
- Mutations can give rise to new versions of a gene (called alleles) and hence change the characteristics of an organism
- Only germ line mutations (in gametes) produce heritable variation,somatic mutations (in body cells) are not passed to offspring
Point Mutations
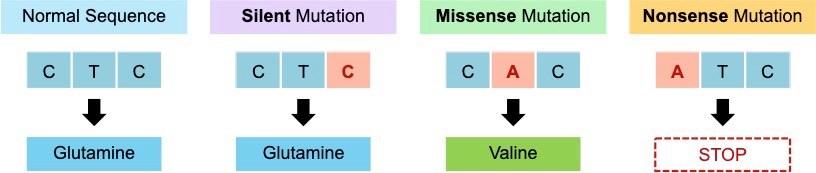
Point mutations involve the substitution of a single base of DNA, which may alter the phenotype by changing the protein sequence
- Silent mutations occur when the DNA change does not alter the amino acid sequence (due to degeneracy of the genetic code)
- Missense mutations occur when the DNA change alters a single amino acid in the polypeptide chain (can create new alleles)
- Nonsense mutations occur when the DNA change creates a premature STOP codon which truncates the polypeptide
Frameshift Mutations
Frameshift mutations involve either the addition (insertion) or removal (deletion) of a single base of DNA, changing the reading frame
- This change will affect every codon beyond the point of mutation and thus may dramatically change the amino acid sequence

Block Mutations
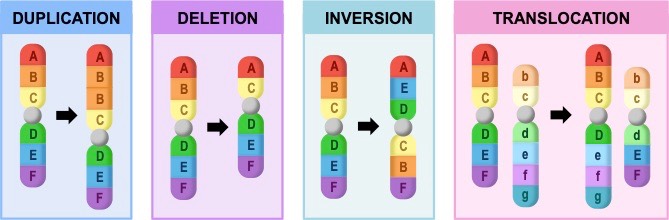
Block mutations are changes to segments of a chromosome, resulting in large scale changes in the DNA of an organism
- Block mutations are commonly caused by transposons (mobile genetic elements that can change positions within the genome)
There are many different types of block mutations that can exist, including:
- Duplications – a part of the chromosome is copied, resulting in duplicate segments (potentially increasing gene expression)
- Deletions – a portion of a chromosome is lost (along with any genes contained within this segment)
- Inversions – a segment of a chromosome is removed and then replaced in reverse order
- Translocations – segments of two chromosomes are exchanged (may interrupt gene sequences)
Gene Flow
Mutations are the only source of new alleles within a population, however alleles can also be introduced from other populations
- The movement of alleles between interbreeding populations (as a result of migration and sexual reproduction) is called gene flow
- Gene flow maintains the genetic compatibility between two separate populations and hence functions to prevent speciation